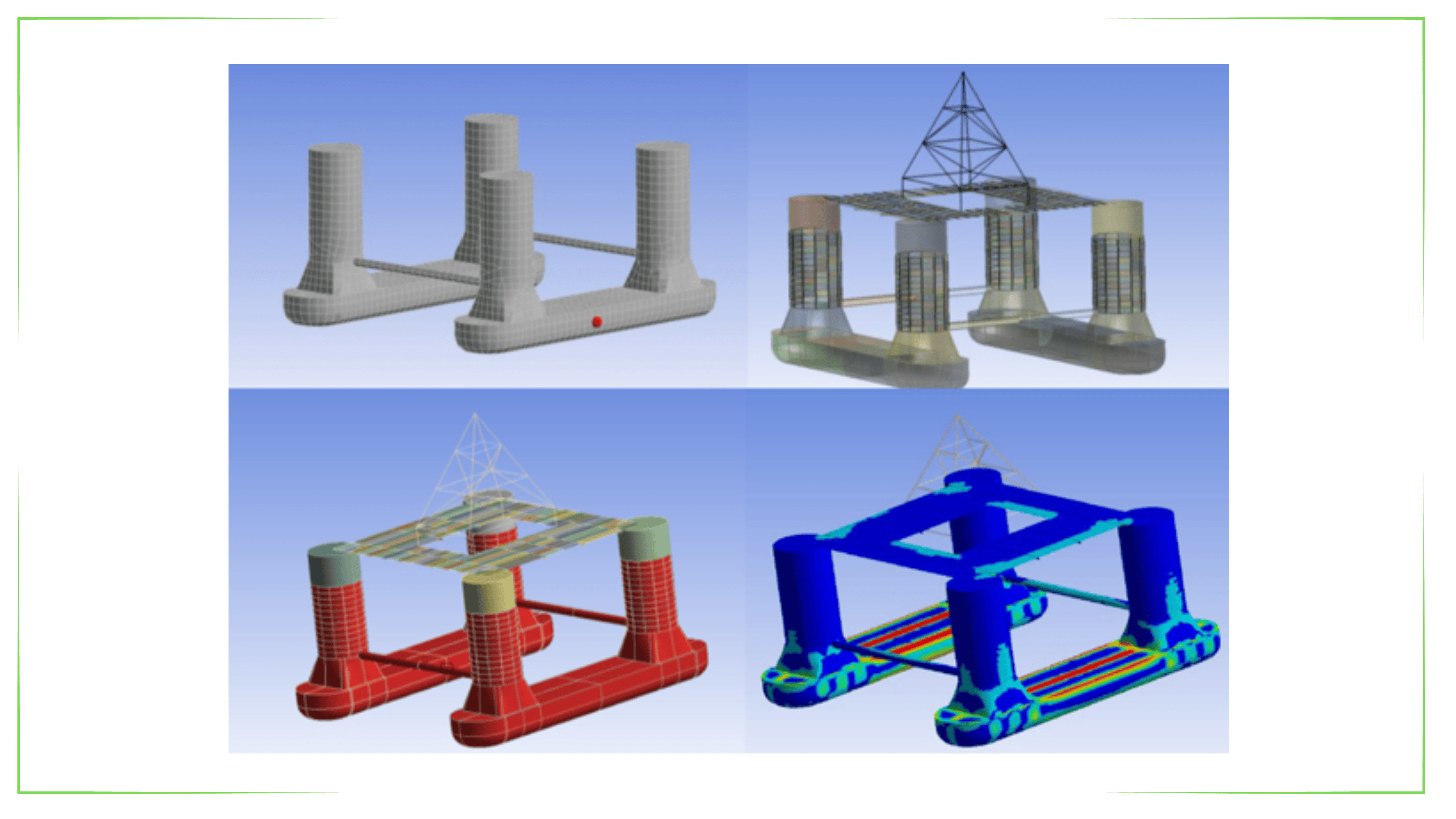
Hydrodynamic Analysis
Hydrodynamic analysis is an engineering discipline that studies how floating structures (ships, platforms, docks, etc.) respond to external forces such as waves, currents and wind in the marine environment. This analysis is critical in the design phase by simulating the behavior of the floating structure at sea.
The main objective of hydrodynamic analysis:
To evaluate the stability and safety of the floating structure against external forces such as waves, currents and wind.
To predict the motions (rocking, pitching, vertical motion) and velocity of the structure.
To determine the loads (inertial loads, compressive loads, mooring loads) required for future structural analysis.
Methods used in hydrodynamic analysis:
Potential Flow Theory: This method is used to model the behavior of the floating structure under idealized flow conditions.
Viscous Flow Analysis: This method is used to model the behavior of the floating structure considering realistic flow conditions (such as viscosity and turbulence).
Experimental Methods: Experimental facilities such as wind tunnels and wave pools are used to observe the behavior of the floating structure and validate the hydrodynamic analysis.
Benefits of hydrodynamic analysis:
Helps design safer and more efficient floating structures.
Helps prevent marine accidents.
Helps reduce structural repair and maintenance costs.
Contributes to the development of more environmentally friendly maritime transportation solutions.