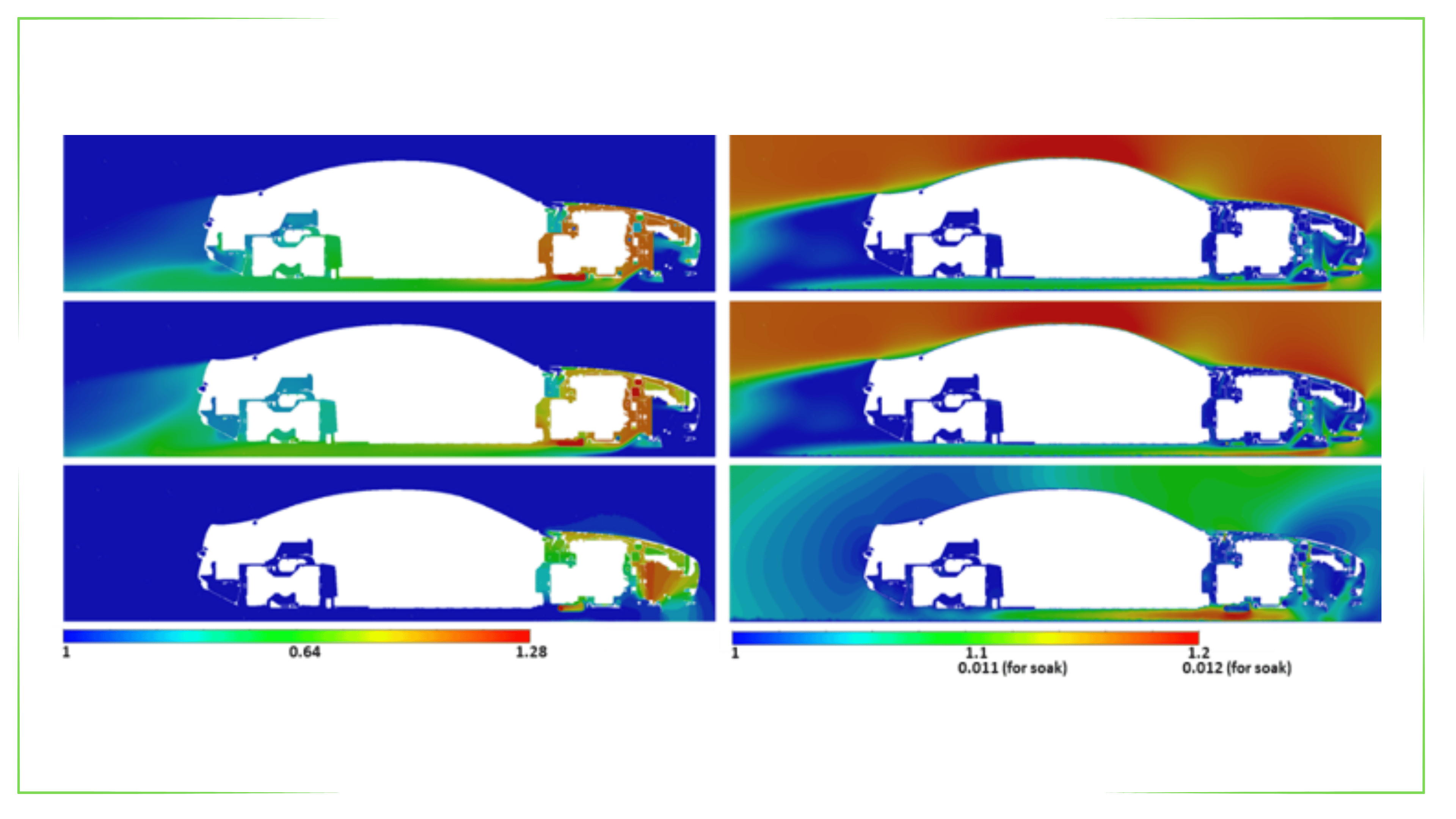
Thermal Analysis
Thermal Analysis with Finite Element Method (FEM) is a powerful engineering tool used to study the heat transfer of components and assemblies with complex geometries. This method allows to determine the temperature and heat flow distribution of components and assemblies, considering the three main heat transfer mechanisms: conduction, convection and radiation.
Benefits of Thermal Analysis:
Allows complex geometries to be analyzed.
Faster and cheaper compared to experimental testing.
Enables better product design and optimization.
Makes it possible to identify and solve potential thermal problems in advance.
Types of Thermal Analysis:
Linear Thermal Analysis: Used when thermal properties are constant.
Non-Linear Thermal Analysis: Used when thermal properties are variable.
Steady State Thermal Analysis: Used when thermal loads are independent of time.
Time Dependent Thermal Analysis: Used when thermal loads are time dependent.
Usage Areas of Thermal Analysis:
Electronic devices: Thermal design of electronic devices such as computers, cell phones, televisions.
Automotive: Thermal analysis of automotive components such as engines, exhaust systems, brake systems.
Aircraft and spacecraft: Thermal analysis of aerospace vehicles such as airframes, engines, rockets.
Buildings: Thermal insulation and energy efficiency analysis of buildings.
Solar energy systems: Thermal performance analysis of solar panels.
Thermal Analysis Services with Finite Element Method:
Thermal analysis of components and assemblies with complex geometries.
Linear and nonlinear thermal analysis.
Steady-state and time-dependent thermal analysis.
Heat flow and temperature distribution simulations.
Solution and optimization of thermal problems.