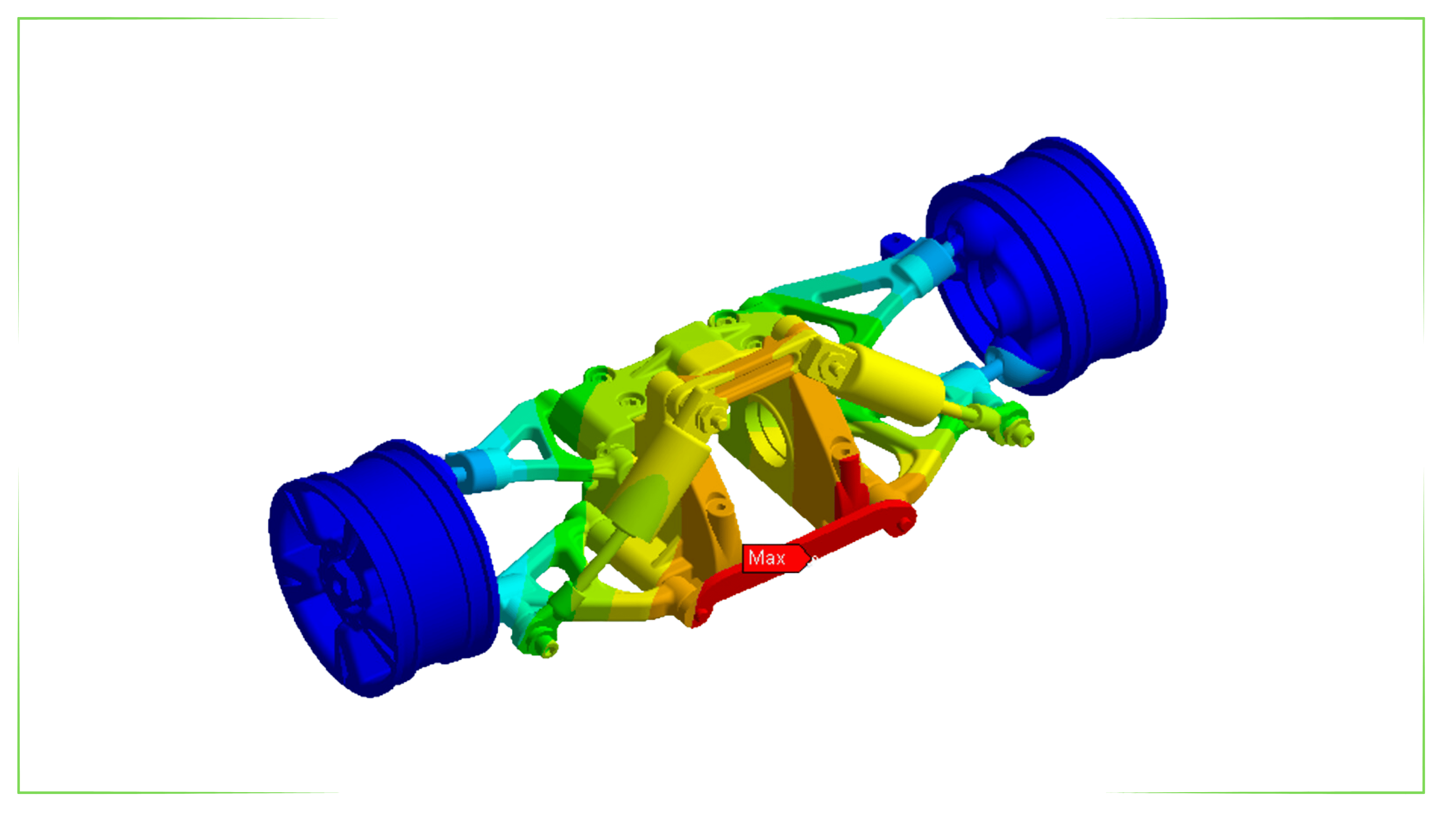
Structural Analysis
Structural analysis is a fundamental engineering discipline used to assess the safety and robustness of engineering designs such as buildings, bridges, machinery and other structures. These analyses use mathematical models and computer simulations to predict how the structure will behave under static and dynamic loads.
Static and Dynamic Analysis:
Static analysis examines the behavior of structures under time-independent loads (e.g. gravity, dead loads). This type of analysis is the most widely used analysis method for the design of buildings and other static structures.
Dynamic analysis studies the behavior of structures whose loading conditions vary as a function of time (e.g. earthquakes, wind loads, vibrations). This type of analysis is important for the design of complex structures such as bridges, towers and other structures subjected to dynamic loads.
When is Dynamic Analysis Necessary?
As a general rule, dynamic analysis is recommended when the rate of loading is greater than 1/3 of the lowest natural frequency of a component. Natural frequency means the frequency at which a structure vibrates spontaneously. If the rate of loading is higher than the natural frequency, it becomes important to consider dynamic effects such as inertia and damping of the structure.
Some important examples of dynamic analysis:
Earthquake analysis: Used to predict the behavior of buildings and other structures under earthquake loads.
Wind analysis: Used to predict the behavior of bridges, towers and other structures under wind loads.
Vibration analysis: Used to predict the behavior of machines, motors and other vibrating systems.
Benefits of structural analysis:
Helps design safer and more durable structures.
Helps to predict structural failures.
Helps reduce repair and maintenance costs.
It enables more economical designs with lighter weight and less material usage.